how is biodiversity beneficial to humans
As most of the minerals are used by the biotic community of an ecosystem the nutrient loss is prevented. Biodiversity is Good for the Economy.

European Commission Science For Environment Policy Multimedia Ap Environmental Science Ecosystems Ecosystems Projects
To understand why biodiversity is important we have to think like biologists.

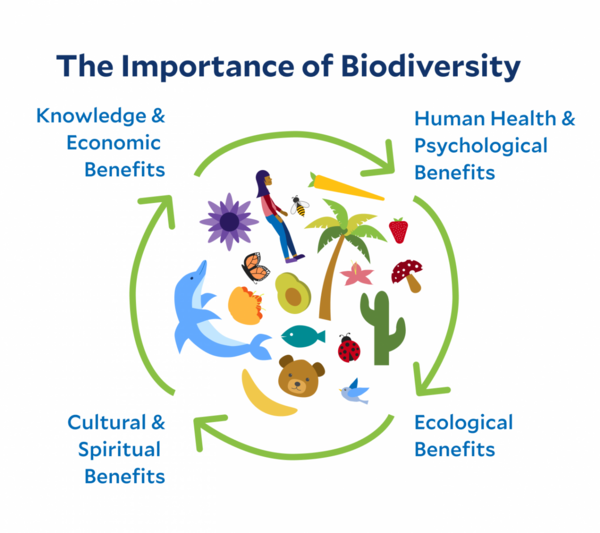
. Biodiversity is essential for the processes that support all life on Earth including humans. Learn why biodiversity is important and how it benefits both human beings and the planet. Biodiversity gives resiliencefrom the microbes that contribute to the formation of the human biome to the genes that help us adapt to stress in the environmentsupports all forms of livelihoods may help regulate disease and is necessary for physical mental and spiritual health and social well-being.
Land use change pollution poor water quality. Another good reason to conserve biodiversity is that it is good for the economy. The minerals remain in the soil while organic matter lies on the forest floor.
The rich biodiversity in the tropics is sustained largely by recycled nutrients. Scientificbiodiversity represents a wealth of systematic ecological data that help us to understand the natural world and its origins. Secondary plant compounds animal toxins and antibiotics produced by bacteria and fungi.
The biodiversity book by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation. Without a wide range of animals plants and microorganisms we cannot have the healthy ecosystems that we rely on to provide us with the air we breathe and. I thought that with 30 years of good science we could address these problems but I was wrong.
Biodiversity can be explored in a. For example potatoes were domesticated beginning around 7000 years ago in the central Andes of Peru and Bolivia. Therefore many businesses are at serious risk due to biodiversity loss.
It also supports economic opportunities and leisure activities that contribute to overall wellbeing. The loss of biodiversity is itself a threat to public health In 2015 the Earth Island Journal asserted unequivocally that biodiversity limits disease outbreaks among humans and wildlife Proponents of the theory believe the dilution effect is widespread and they champion human health policies that include conservation initiatives. In ecosystem of low biodiversity the uptake of nutrient is not so efficient.
Since the beginning of human agriculture more than 10000 years ago human groups have been breeding and selecting crop varieties. This term can also refer to the idea of how many different species interact with one another in a certain space which can also be known as a habitat. Loss of biodiversity will impact the number of pharmaceuticals available to humans.
The impact of all the main drivers of biodiversity loss is accelerating and as a consequence so is the pace of biodiversity decline. About 175 million species of plants animals and microorganisms have been identified out of the 13 million total species estimated by scientists Sustaining 2000. On a global scale however biological diversity -- or biodiversity -- is vitally important to the health of our planet and humanity.
Unlike nonscientists biologists dont think of biodiversity strictly in terms of the number of species found on Earth. This crop diversity matched the cultural diversity of highly subdivided populations of humans. What are the conditions under which biodiversity is good for human infectious disease risks and when does biodiversity serve as a spark for emergence of disease in human populations.
Biodiversity is important to humans for many reasons. Biodiversity is key to a sustainable ecosystem for all of creation how do we ensure not to harm it. The term biodiversity is known as the amount of variety that exists in a specific habitat ecosystem andor the world.
Benefits of Biodiversity to Humans. The services these species provide contribute to the delicately-running natural cycles that help make earth. The list of services ecosystems perform for us is extensive and includes.
The benefits of biodiversity to humans are sometimes called. In figure 4 we present a unified framework that includes both the effects of human development on biodiversity and well-being and feedbacks from biodiversity to HWB. Humans use many compounds that were first discovered or derived from living organisms as medicines.
The top environmental problems are selfishness greed. Biodiversity is also key for the continued provision of ecosystems services it provides which serve both humans and the systems themselves although the term is largely used in relation to the benefits reaped by us. From this unified framework it becomes clear that development will be sustainable when it strives to minimize harmful feedbacks and ideally turns them into beneficial feedbacks.
Benefits to societies from biodiversity include material welfare security of communities resilience of local economies and human health. Growing demand for natural resources due to the increasing human population more rapidly increasing per capita consumption and changing consumption patterns has meant that ever more natural habitat is being. Biodiversity is also considered by many to have intrinsic valuethat is each species has a value and a right to exist whether or not it is known to have value to humans.
According to the World Economic Forum more than half of the worlds total GDP of 44 trillion is modestly or highly dependent on nature. In 2015 the Earth Island Journal asserted unequivocally that biodiversity limits disease outbreaks among humans and wildlife. We will engage with this important topic in a debate format focusing on views that engage biodiversity as a beneficial ecosystem service.
As of now scientists believe that there are about 100. Biodiversity supports human and societal needs including food and nutrition security energy development of medicines and pharmaceuticals and freshwater which together underpin good health. Ecosystem services provided by biodiversity.
More medicines are expected to be discovered in nature.

Biodiversity Why Is Biodiversity So Important
Yale Experts Explain Biodiversity Yale Sustainability

Infographic Ecosystem Services Ap Environmental Science Ecosystems Environmental Education

Planted City Ecosystems Ecological Economics Landscape And Urbanism

Biodiversity Why Is Biodiversity So Important

Reforestation Biology Projects Ecosystems Biodiversity

Enviroatlas Benefit Category Biodiversity Conservation Us Epa

Genetic Diversity The Hidden Secret Of Life Convention On Biological Diversity

Why Is Biodiversity Important And How Does It Help Us Survive Developmentaid

Issues Ecotools Ecosystems Ap Environmental Science Environmental Education

Extinction Biodiversity The Conscious Challenge

Infographic Ecology The Study Of The Place We Live Teaching Ecology Environmental Science Ecology

Conservation Preventing Biodiversity Loss Saving Earth Encyclopedia Britannica

Forests Desertification And Biodiversity United Nations Sustainable Development

Threats To Biodiversity Infographics Environmental Science Lessons Environmental Education Biodiversity
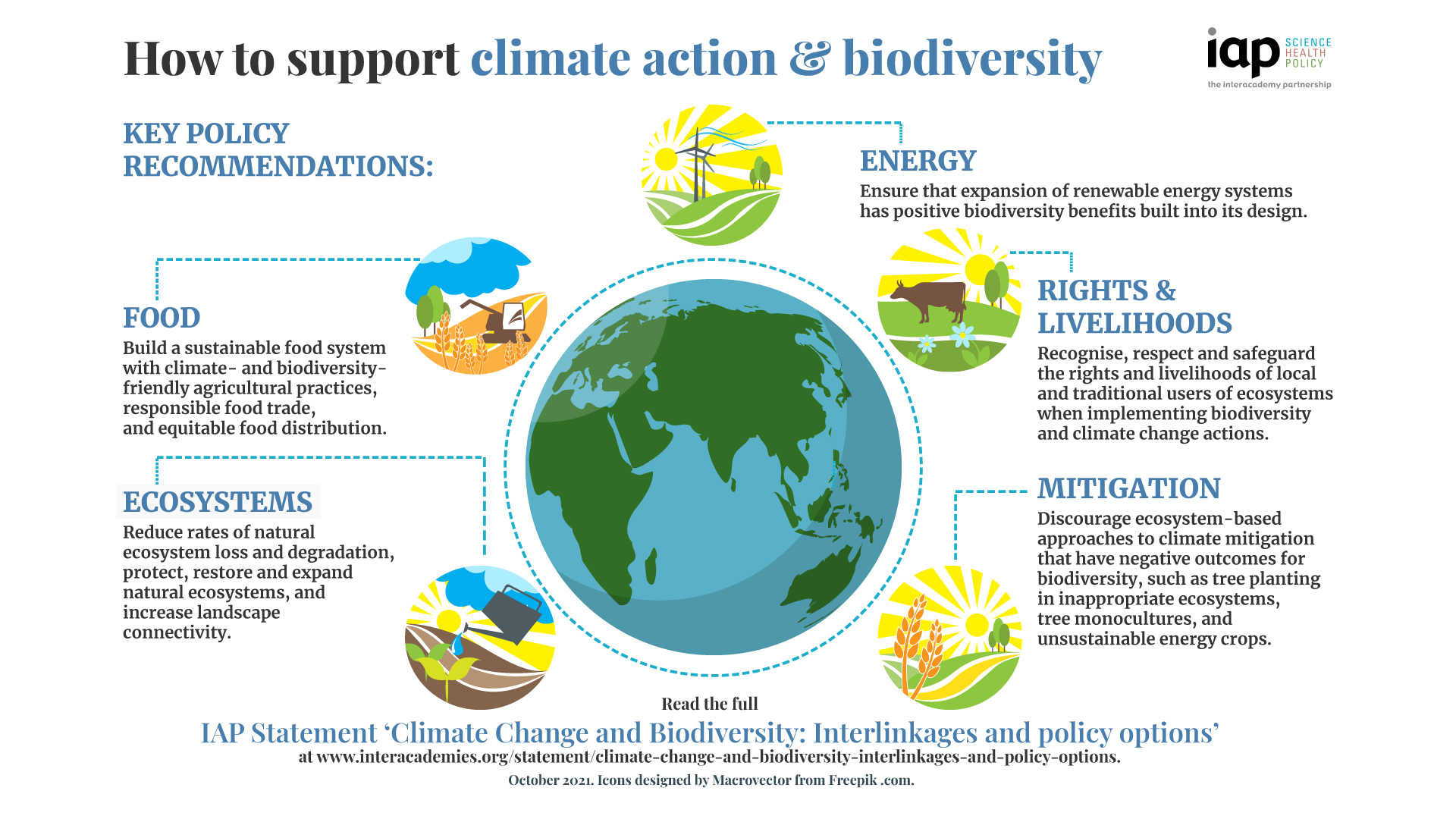
Climate Change And Biodiversity How To Support Climate Action And Biodiversity Infographic


